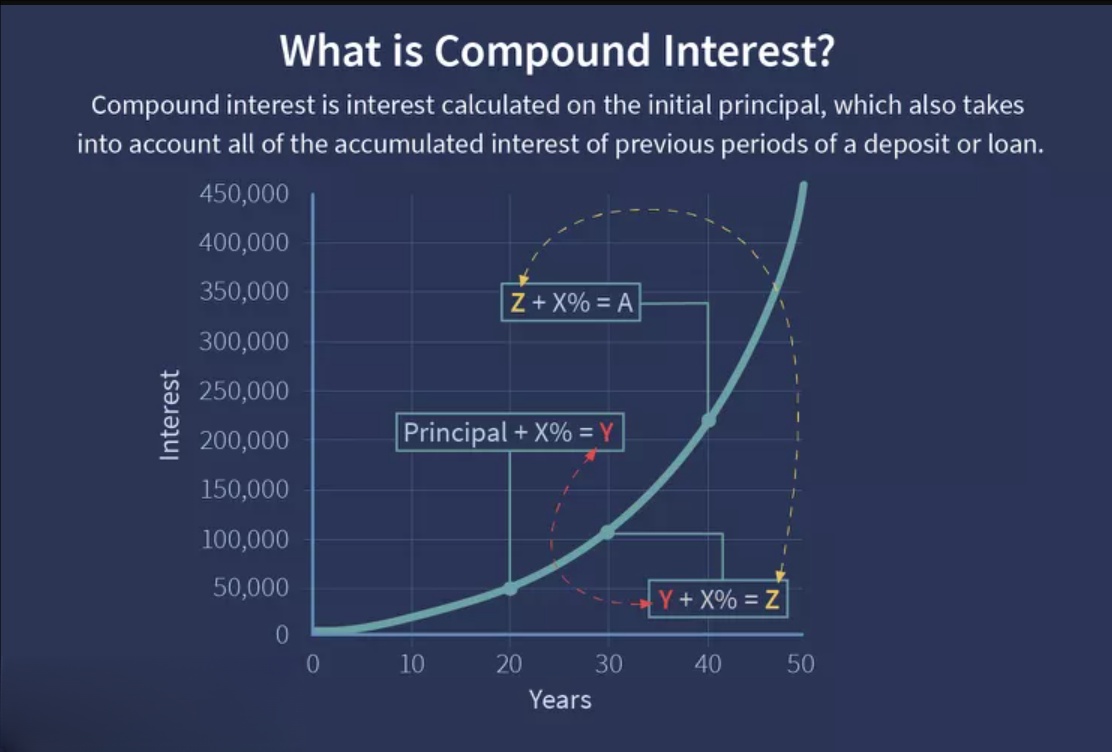
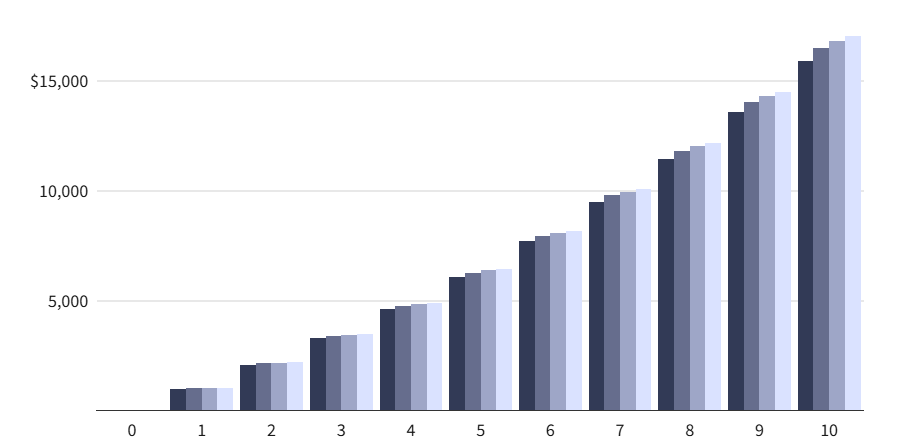
Compound Interest Calculator
A powerful tool to calculate the future and present value of your investments with compound interest.
Note: Present Value (PV) is typically calculated for a lump-sum investment to determine the initial capital needed to reach a future goal.